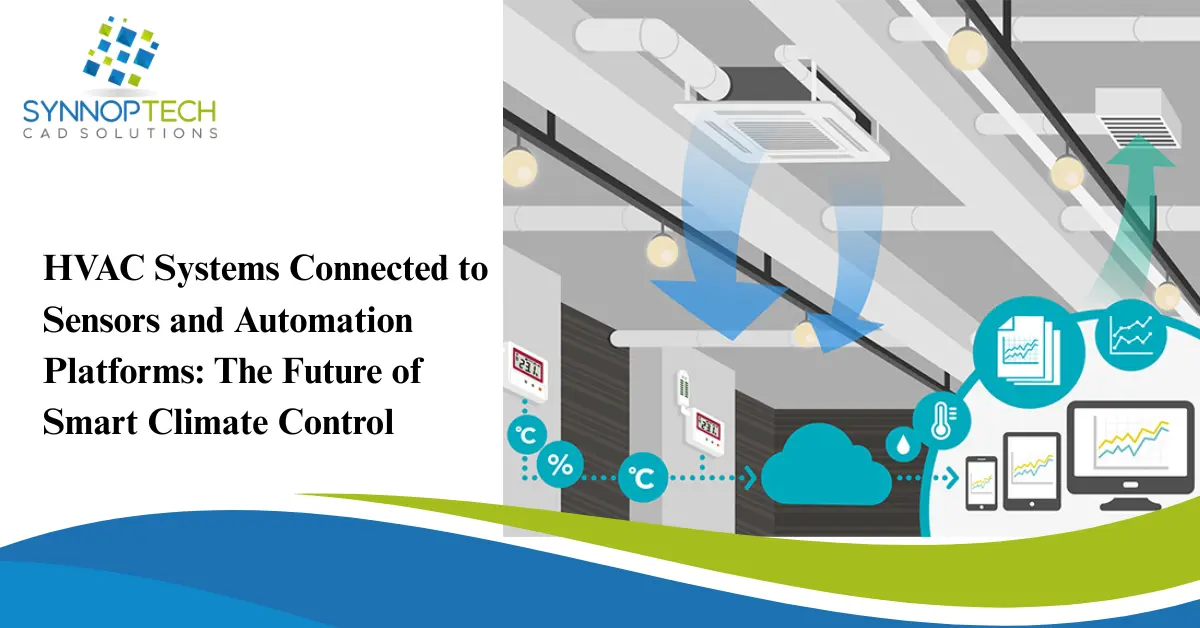
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are no longer limited to just heating or cooling a space. Today, they are evolving into intelligent, connected ecosystems powered by sensors and automation platforms. This change is redefining how buildings manage comfort, energy efficiency and operational performance.
From commercial complexes and hospitals to smart homes and industrial facilities, sensor-enabled HVAC systems are becoming a cornerstone of modern infrastructure.
What Does a Sensor-Connected HVAC System Mean?
A sensor-connected HVAC system uses a network of smart sensors to collect real-time data from different areas of a building – such as temperature, humidity, air quality, occupancy and pressure sensors. This data is processed through automation platforms or building management systems (BMS) to take intelligent decisions without manual intervention.
Instead of relying on fixed schedules or manual thermostats, the system continuously adapts based on actual conditions and usage patterns.
Key Sensors Powering Modern HVAC Systems
Smart HVAC automation relies on multiple types of sensors working together:
- Temperature sensors ensure precise climate control in different zones.
- Humidity sensors maintain optimal moisture levels for comfort and health.
- Occupancy sensors detect whether a space is in use and adjust airflow accordingly.
- Air quality sensors monitor CO₂, VOCs, and pollutants to improve indoor air quality.
- Pressure sensors optimize airflow and detect system blockages or leaks.
Together, these sensors provide a complete picture of a building’s indoor environment.
How Automation Platforms Bring Everything Together
Automation platforms act as the brain of smart HVAC systems. They collect sensor data, analyze patterns, and trigger automated responses. For example, if occupancy sensors detect an empty meeting room, the system can reduce airflow and temperature, saving energy without compromising comfort.
Advanced platforms also use cloud connectivity and AI-driven analytics to:
- Optimize energy consumption
- Predict equipment failures
- Enable remote monitoring and control
- Integrate with lighting, security, and access control systems
This level of integration transforms HVAC from a standalone utility into a strategic asset.
Benefits of Sensor-Driven HVAC Automation
1. Improved Energy Efficiency
By responding to real-time conditions instead of static settings, smart HVAC systems significantly reduce energy waste. This leads to lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
2. Enhanced Occupant Comfort
Zoned climate control ensures that different areas maintain their ideal temperature and airflow, improving comfort for occupants throughout the day.
3. Predictive Maintenance
Sensors can detect performance issues—such as abnormal temperature fluctuations or pressure drops—before they become major problems. This allows maintenance teams to act proactively, reducing downtime and repair costs.
4. Better Indoor Air Quality
Air quality sensors automatically trigger ventilation adjustments when pollutant levels rise, creating healthier indoor environments, especially in offices, schools, and healthcare facilities.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
Facility managers gain access to dashboards and reports that provide insights into system performance, energy usage, and optimization opportunities.
Integration with IoT and Smart Building Ecosystems
Modern HVAC automation platforms are increasingly part of larger Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystems. They communicate with smart meters, renewable energy systems, weather forecasting tools, and even utility grids.
For example, an HVAC system can pre-cool a building during off-peak energy hours or adjust settings based on upcoming weather conditions—maximizing efficiency and sustainability.
Challenges to Consider
While the advantages are compelling, implementing sensor-connected HVAC systems requires careful planning. Initial setup costs, cybersecurity considerations, system compatibility, and staff training are important factors to address. However, for most organizations, the long-term operational savings and performance gains far outweigh the challenges.
The Future of HVAC Automation
As AI, machine learning, and edge computing continue to advance, HVAC systems will become even more autonomous and predictive. Future systems will not only react to conditions, but also anticipate needs—occupier behavior, seasonal trends, and energy pricing—to deliver optimal performance at all times.
Summary: HVAC systems connected to sensors and automation platforms represent a major shift toward smarter, more sustainable buildings. By combining real-time data, intelligent controls and seamless integration, these systems provide improved comfort, lower energy consumption and long-term cost savings.
For businesses and homeowners alike, investing in smart HVAC automation is no longer a luxury—it’s a strategic move toward a more efficient and intelligent future.