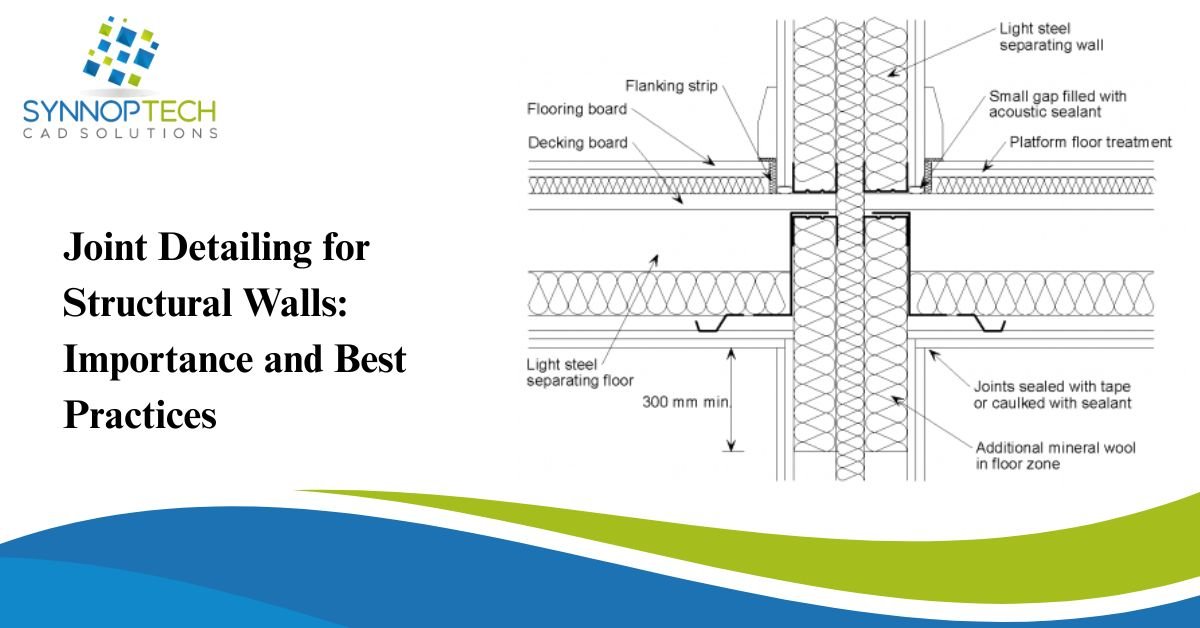
The process of joint detailing is vital in every structural engineering project, as it shields a structure from damage, makes sure it is safe to use, and helps it withstand the test of time. Regardless if a structure employs reinforced concrete, masonry, or steel, detailing the interface of walls, slabs, beams, and other structural features is a prerequisite to ensure the structure performs as intended.
Structural walls must withstand multiple different forces, including vertically applied loads, lateral loads (from wind or seismic activity), thermal changes, and ground settlement. To address both of these constraints, careful attention must be paid to the detailing of the joints in relation to the structural movements. This is the focus of the joint detailing of structural walls and the reason why achieving the best design practices is necessary.
1. What are structural wall joints?
Structural wall joints are the spaces classified as gaps that are conceded between the two connected structural members (two walls, or a wall and a slab) and are meant to accommodate different types of movements (thermal, settlement, and shrinking). These joints are functional or serve a purpose by aiding in the transfers of loads and maintaining the structural integrity of a building.
types of joints in structural walls
Expansion Joints: These are made to allow expansion or contraction of materials due to temperature changes.
Contraction Joints: Controls cracks that may occur due to the shrinkage of concrete in the curing process.
Movement Joints: These allow lateral or angular changes due to seismic forces, settlement, or thermal changes.
Control Joints: These focus on determining the location of cracks in a masonry or concrete wall.
2. Why the Detailing of Joints in Structural Walls Is Important
The following are reasons why joints should be well-detailed:
a. Load Transfer
The joints help to ensure the loads coming from slabs, beams, and other structural parts are balanced properly along walls. Joints that are poorly detailed result in unbalanced loads and will compromise the integrity of the structure.
b. Accommodation of Movements
All building structures are subjected to different types of movements. These may result from temperature changes, shrinkage, or settlement of the materials. Joints are intended to allow for such movements without cracks or other damage to the wall system. Structural damages may occur due to the absence of appropriate joint detailing.
c. Stopping Cracking from Happening
Wall cracking is often due to poor detailing of concrete and masonry walls. Adequate detailing of joints helps engineers to manage where cracks will take place. With proper detailing, cracks will only be permitted to develop in designated areas, such as contraction joints, which reduces damage to the rest of the structure.
d. Long-Term Care and Endurance
Well-designed and executed joints can safeguard from considerable long-term damage to a structure. For instance, mechanized expansion joints are instrumental in controlling stress-related factors that may otherwise compromise the walls or result in moisture infiltration, which facilitates deterioration.
3. Important Features in Detailing Joints for Structural Walls
a. Position of the Joints
Placement of joints is critical, as they must achieve the objectives for which they were designed. The following are the most common areas that joints tend to be positioned:
Where walls and floors intersect, to permit relative movement between walls and floors.
Between materials or structural components (for instance, a concrete wall intersects with a steel column) to permit varying rates of expansion.
Within the windows and doors and other openings to intercept cracking due to different rates of settlement.
Within zones of high seismic or wind forces to allow for flexibility and protect against dynamic forces.
b. Joint Width and Spacing
Estimating the width requires consideration of the anticipated movement, including expansion, contraction, or even settling. Spacing joints requires balancing consideration of the material of the wall in question and the dimensions of the building as a whole. Some cases include:
Due to the nature of concrete walls, these structures tend to need both wider and more spaced joints in comparison to other materials.
In comparison to concrete walls, masonry walls need smaller joints, but these require meticulous detailing in order to maintain defense against moisture ingress.
c. Reinforcement at Joints
The addition of reinforcement in the joints assists in controlling cracks and ensures the wall structure is not compromised. Depending on the wall and the expected stresses on the joint, different types of reinforcements, ranging from rebar to mesh, may be utilized. Properly placing reinforcement in the joint areas is critical to controlling lateral stresses and repairing movement issues.
d. Joint Sealants
Joint sealants play a critical role in moisture ingress prevention. Most sealants that have the capability of functioning as a joint sealant help prevent moisture ingress and loss. For example, in walls of concrete or masonry, the use of elastomeric sealants in the expansion joints ensures that flexibility is maintained but does not allow the ingress of water.
Selection of the sealant should consider the following:
- Movement capacity: In some cases, the sealant must allow for significant expansion or contraction.
- Environmental exposure: Sealants must remain effective under specific conditions, such as UV exposure, chemicals, or freezing temperatures.
e. Detailing for Seismic and Wind Loads
In regions prone to seismic activity or strong winds, the detailing of the joint exhibits greater importance. A movement joint must allow for the forces produced by the earthquake or extreme wind activity. The design should provide that:
- The wall structure dissipates the lateral forces without failure.
- Joints freely allow flexing and displacement without any possibility of cracks, which may cause safety concerns.
f. Waterproofing and Insulation
Effective waterproofing at construction joints is critical to restrain water ingress that can weaken the structure and cause the corrosion of the steel reinforcement. Insulation materials can also be placed within joints to minimize energy loss by reducing thermal bridging, which is critical for energy-efficient buildings.
4. Recommended Guidelines for Structural Wall Joint Detailing
Here are some strategies that the audience needs to follow to join detailing in structural walls:
Perform thorough analyses: Analyze the appropriate load conditions and material properties, considering all structural factors, to determine appropriate joint layouts with spacing and reinforcement.
Cooperation with other job functions: Check that other disciplines such as HVAC, electrical, and plumbing are not going to clash with the joint detailing.
Consideration of material associated with the joint: Concrete and masonry material associated with the joint comes with its different properties; thus, expansion, contraction, or shrinking needs to be a factor of consideration for the chosen joint types.
Accessibility for servicing: Joints that sealants need maintenance to be reapplied to need to be designed to allow easy inspection and maintenance.
Adhere to local legislation: Joints need to comply with local building codes and regulations and specific design parameters to ensure buildings withstand relevant climatic conditions.
Conclusion
Effective joint detailing ensures that structural walls will be safe, secure, and withstand the test of time. Well-designed joints balance structural movement, efficient load transfer, and the prevention of cracks, moisture intrusion, and damage throughout the structure’s life. Adhering to proper engineering practices improves the performance and durability of structural walls, ultimately enhancing the value of the entire building project.